The services to consider are gmail.com, mail.yahoo.com, hotmail.com, flikr.com, facebook.com, twitter.com, plus.google.com, etc, etc, etc, etc
But let's focus on email for the moment.
In my case I'm writing a book (it's almost done! famous last words of the book author) and the process was emailing chapters back and forth with my editors all the time. Each round of work on a chapter meant the editor sending an email, with the chapter attached, I work on it for awhile, then send a reply email with the chapter attached. The chapters are usually 1/2 megabyte in size so there's a megabyte of additional email storage required each time we exchange edits on a chapter. With 6 chapters (it's a short book) and several exchanges during the life of working on the book, we're talking about 20+ megabytes of total storage just for the attachments on the emails sent related to this book. And because this is related to a contract I signed, I'm likely to keep these emails archived for a long time to come. But in practice I'll probably never refer to them again.
Yup, 20+ megabytes of data storage that's likely to remain in my email for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time but unlikely to ever be used.
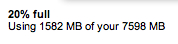 That may seem like a tiny amount and maybe you're concerned about my sanity. But first, as you see here gmail is kind enough to tell me that I have 1.5GB of email stored in this account. Second, just how many email customers does Google have? It's not just gmail but the other services I mentioned above, and the model to store "everything" for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time.
That may seem like a tiny amount and maybe you're concerned about my sanity. But first, as you see here gmail is kind enough to tell me that I have 1.5GB of email stored in this account. Second, just how many email customers does Google have? It's not just gmail but the other services I mentioned above, and the model to store "everything" for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time.
The cloud computing providers have done a good job of hiding the effect or impact of storing our digital online stuff. Before services like gmail.com or mail.yahoo.com we had an email client on our personal computer and that email client stored email on the computers hard drive. We directly paid the cost of keeping email around through buying a large-enough hard drive in the computer, remembering to back up the computer, and pulling our hair out when the computer dies and we hadn't backed up the computer. It's not just email, it's the other things, pictures, documents, spreadsheets, etc.
Cloud computing is the new wave of the Internet (gmail.com, mail.yahoo.com, hotmail.com, flikr.com, facebook.com, twitter.com, plus.google.com, etc, etc, etc, etc) and one thing these services offer us is freedom from maintaining our own machines. We just use services over the Internet to access our stuff, rather than storing our stuff on our own machine. Not only do we not have to pay for a fancy machine just to do email and a few pictures, we can trust the cloud to store our stuff for us.
But cloud computing doesn't come for free, and it carries an environmental impact.
It may be called "the cloud" but that doesn't mean its a white puffy thing up in the sky with no actual substance. Trust me, "the cloud" is constructed of computers and routers and cables and racks and air conditioning in colocation facilities around the planet.
Every email attachment that's stored for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time but unlikely to ever be used represents the cloud infrastructure becoming bigger. Because of this book and the chapters sent back and forth, Google will be holding an additional 20+ megabytes of data inside my gmail account. So what, you might say, I'm well under the 7GB storage limit they gave me, what's the big deal! The big deal is in the aggregate, the cost of all the email being stored, and the ever-increasing storage requirements to store "the cloud".
For example, every tweet ever uttered is stored in twitter.com's infrastructure. Plus all those tweets are being sent to partners such as the Library of Congress. How many tweets are twittered every day? And as a result to the traffic twitter.com carries, how much additional data storage units are they buying per day?
The data storage units are, well, disk drives in a "storage array" plus some sort of backup system. Perhaps the backup system is a second storage array, and maybe a third storage array. Maybe instead it's tape drives with data stored on digital tape. To run a stable robust service that the public will trust to reliably store their stuff for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time, the service provider has to build in redundancy and the ability to recover from failures. What if the main storage array dies taking with it all of twitter.com's tweets? What would be the loss to society of all those tweets vanishing in a cloud of electronic smoke? Hence, twitter.com has to have a system in place for recovering as many tweets as possible and quickly getting back to the job of facilitating the twitter.com conversation.
The same can be said for the other cloud services. Facebook stores all the old conversations and interactions even though they make it incredibly impossibly difficult to access them. Flikr, Youtube, etc, store all sorts of videos and pictures for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time. That video you shot of a cute cat doing something strange, by uploading it to Youtube you obligated Google to maintaining an extra 20+ Megabytes of storage (video files are big) for a lo-o-o-o-o-ng time.
Each unit of computing infrastructure consumes electricity, not just to run the machine but to power the air conditioning unit keeping the machines cool. It's said that cooling is the biggest energy cost of running the Internet.
Each unit of computing infrastructure is built out of metal, plastic and various other materials including some that are exceedingly rare.
In other words the cloud isn't free, and the cloud will have a growing environmental impact. The electricity and other resources required to run the cloud is not free, and it's polluting our environment.
